Partho P. Sengupta, MD, DM
- Associate Professor of Medicine
- Director of Noninvasive Cardiology
- Department of Medicine
- University of California Irvine
- Irvine, California
Ultrasound can also be used to assess fetal well-being through evaluation of fetal body and breathing movements in addition to the amniotic fluid volume anxiety zoloft luvox 100 mg with visa. Developments in ultrasound technology and our understanding of fetal physiology have led to continuing refinement of the use of Doppler studies in obstetric care anxiety symptoms burning skin generic luvox 100mg fast delivery. Largely limited to studies of the umbilical and uterine arteries in the 1980s anxiety 101 cheap 100 mg luvox with amex, modern Doppler techniques can include not only studies of fetal arteries but also venous blood flow to help identify fetuses at the highest risk for stillbirth and serious complications (see Assessment of Fetal Well-Being anxiety images buy cheap luvox 50mg on line, page 25) Though obstetricians rely on ultrasound fetal weight estimates, these are not accurate in all circumstances. Current research is evaluating the utility of incorporating fetal measurements from 3-dimensional ultrasound to improve our accuracy. Many of these fetuses are simply small but normal, and use of this criterion as the threshold can lead to undue anxiety, testing, and even early delivery of a normal baby. However, these criteria can miss some babies who are actually having trouble growing but are larger. Standard growth charts that are created from large population-based High-Risk Pregnancy Care, Research and Education databases do not take into account factors such as maternal and paternal size, preexisting maternal medical conditions, or racial, environmental, or genetic factors that can affect fetal size. Several research groups have pursued the study and development of customized growth curves that identify the growth potential for an individual fetus based on some of these characteristics. These studies are examining the value of customized growth curves to identify fetuses at risk for complications because of abnormal growth. Advances in ultrasound technology have increased our ability to evaluate fetal body composition by measuring both fetal fat and lean body mass. Measurements of the fat of the fetal arm, thigh or abdomen, for example, could allow us to better understand which fetuses are undernourished versus those that are small but normal. In diabetic pregnancies the presence of additional fat stores might suggest that glucose control is not adequate. A standard for normal fetal growth that leads to a life course that is as healthy as possible has never been established. Defining this standard and improving the accuracy of estimating fetal weight are primary goals of the National Standard for Normal Fetal Growth project, launched by the National Institutes of Health in 2009. The study will develop individualized growth standards that incorporate factors including race/ethnicity and maternal characteristics. An international multicenter study with similar objectives is planned by the World Health Organization. Considerable racial disparity exists- stillbirth is more than twice as common among African-Americans than Caucasian women (11. Other maternal risk factors for stillbirth include advanced age, obesity, and coexisting medical disorders such as diabetes or hypertension. The possible impact of environmental exposures on stillbirth risk remains unknown. Of known stillbirth causes, the most common are genetic abnormalities, alterations in the number or structure of the chromosomes, maternal infection, hemorrhage, and problems with the umbilical cord or placenta. Knowledge about the causes and prevention of stillbirth has been hampered because postmortem investigations are often not done, and the evaluations that are done are not uniform. A detailed postmortem evaluation after stillbirth is important not only to determine the cause but also for developing strategies to prevent a recurrence. One of the most useful evaluations is an autopsy, as this can identify birth defects, abnormalities that likely have a genetic cause, and other potential causes such as infection, anemia, or lack of oxygen. Despite its importance, autopsy is done after only about one-third of stillbirths. Parents often decline an autopsy because of misconceptions about what is done, concerns about how it might affect a planned burial, or concerns about the cost. For families that decide against an autopsy, x-rays or magnetic resonance imaging can sometimes provide useful information and may be an option that is acceptable to them. The second most important assessment to determine the cause of a stillbirth is examination of the placenta. Through this assessment information can be obtained about possible contributing factors such as intrauterine infection, thrombosis in the blood vessels, local placental abnormalities and infarction, and early placental separation from the uterus. Fetal karyotype assessment is also recommended to identify chromosomal abnormalities. Amniocentesis before delivery can be a valuable tool to obtain fetal cells for chromosome analysis. This approach is particularly important if the stillborn is not delivered right away. To address the gaps in knowledge about stillbirth risks and causes, the Stillbirth Collaborative Research network was established in 2003 by the National Institutes of Health.
Usually at the end of the first week of life anxiety symptoms adults discount 100 mg luvox overnight delivery, infected infants become irritable anxiety symptoms watery mouth purchase luvox 50mg otc, feed poorly anxiety symptoms in children discount luvox 100mg without prescription, and develop rigidity with severe spasms anxiety symptoms quitting smoking purchase 50 mg luvox free shipping. Soil, animal feces, and, occasionally, human feces as well as inanimate objects contaminated with spores are the primary source of infection. Risk factors for neonatal tetanus include unvaccinated mothers, home delivery, and unhygienic cutting of the umbilical cord. The following types of wounds are more susceptible to tetanus: (a) grossly contaminated wounds; (b) wounds exposed to saliva or feces; (c) stellate, ischemic, or infected wounds; (d) deep (1 cm) wounds; as well as (e) avulsions, punctures, or crush injuries. Localized tetanus Laboratory Diagnosis Laboratory diagnosis of tetanus like that of C. Laboratory diagnosis is carried out in the patients only to confirm the clinical diagnosis. The disease is confined to the extremity with a contaminated wound and occurs when only the nerves supplying the affected muscle are involved. The condition is characterized by rigidity of muscles, caused by a dysfunction in the interneurons that inhibit the alpha-motor neurons of the affected muscles. Specimens Cephalic tetanus the specimens include excised bits of tissue from the necrotic depths of wounds. The condition usually occurs following head injury or occurs with infection of the middle ear. Symptoms may be localized or may become generalized and include isolated or combined dysfunction of the cranial motor nerves, most frequently the seventh cranial nerve. This is because: Epidemiology Geographical distribution Tetanus is a disease found worldwide. The disease is common in areas where soil is cultivated, in rural areas, in warm and damp climates, and during summer months. Tetanus affects all age groups, with the highest prevalence among newborns and young people. Neonatal tetanus accounts for 50% of the tetanus-related deaths in developing countries. Culture the specimens are inoculated on a blood agar and incubated anaerobically for 2448 hours. Extremely fine translucent film of growth, which tends to swarm over the entire surface of the agar. Produce alpha-hemolytic colonies initially on blood agar, which on prolonged incubation become beta-hemolytic due to production of tetanolysin. Gram-positive bacilli with prominent terminal spores (drumstick appearance) in the Gram-stained smear of the colony. Toxigenicity testing in mouse-a reliable method of identification of the colony as C. Culture is positive in only 30% of cases of tetanus because tetanus is caused only by a few organisms, and many organisms are killed when exposed to air during processing of specimens. Toxigenicity testing in mouse is a reliable method of identification of the colony as C. One-half of the medium is inoculated with tetanus antitoxin (1500 units per mL), while the other half of the medium does not contain any antitoxin. This is due to inhibition of hemolytic activity of the toxin by antitoxin present in the agar. The symptoms begin in mouse with the spatula test: this is most useful and a simple bedside diagnostic test for tetanus. This touch typically elicits a gag reflex and the patient tries to expel the spatula (negative test). The patients develop a reflex spasm of the masseters and bite the spatula if tetanus is present (positive test). Chapter 29 Treatment Treatment of tetanus is (a) initial supportive therapy, (b) wound debridement and care, (c) stopping toxin production, (d) neutralizing unbound toxin, (e) controlling disease manifestations, and (f) managing complications.
Purchase luvox 100 mg overnight delivery. Venom (Eddie's Escape) 4K.
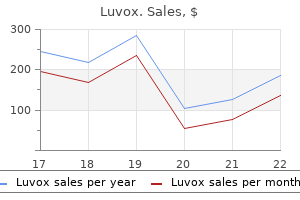
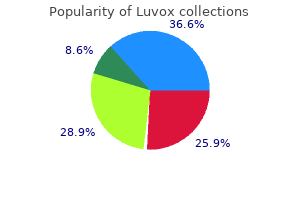
Incidence and risk factors for toxoplasmic encephalitis in human immunodeficiency virus-infected patients before and during the highly active antiretroviral therapy era anxiety symptoms dry mouth luvox 50mg line. Pyrimethamine for primary prophylaxis of toxoplasmic encephalitis in patients with human immunodeficiency virus infection: a double-blind anxiety symptoms journal discount luvox 50 mg without prescription, randomized trial anxiety symptoms in spanish order 100 mg luvox with amex. Toxoplasma gondii infection of the central nervous system: use of the peroxidase-antiperoxidase method to demonstrate toxoplasma in formalin fixed anxiety symptoms uti order luvox 50 mg with visa, paraffin embedded tissue sections. Treatment of central nervous system toxoplasmosis with pyrimethamine/sulfadiazine combination in 35 patients with the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome: efficacy of long-term continuous therapy. Folinic acid supplements to pyrimethaminesulfadiazine for Toxoplasma encephalitis are associated with better outcome. Relative reversal by vitamins (p-aminobenzoic, folic, and folinic acids) of the effects of sulfadiazine and pyrimethamine on Toxoplasma, mouse and man. Maintenance therapy with cotrimoxazole for toxoplasmic encephalitis in the era of highly active antiretroviral therapy. Low incidence of congenital toxoplasmosis in children born to women infected with human immunodeficiency virus. Understanding intestinal spore-forming protozoa: cryptosporidia, microsporidia, isospora, and cyclospora. Pathologic quiz case: a patient with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome and an unusual biliary infection. Threshold of detection of Cryptosporidium oocysts in human stool specimens: evidence for low sensitivity of current diagnostic methods. Treatment of cryptosporidiosis in immunocompromised individuals: systematic review and metaanalysis. Treatment of diarrhea caused by Cryptosporidium parvum: a prospective randomized, double-blind, placebocontrolled study of Nitazoxanide. Multicenter trial of octreotide in patients with refractory acquired immunodeficiency syndromeassociated diarrhea. Evaluation of an animal model system for cryptosporidiosis: therapeutic efficacy of paromomycin and hyperimmune bovine colostrum-immunoglobulin. Paromomycin: no more effective than placebo for treatment of cryptosporidiosis in patients with advanced human immunodeficiency virus infection. Microsporidia: emerging advances in understanding the basic biology of these unique organisms. Modification of the clinical course of intestinal microsporidiosis in acquired immunodeficiency syndrome patients by immune status and anti-human immunodeficiency virus therapy. Analysis of the beta-tubulin gene from Vittaforma corneae suggests benzimidazole resistance. Guidelines for preventing the transmission of Mycobacterium tuberculosis in health-care settings, 2005. Priorities for the treatment of latent tuberculosis infection in the United States. Pulmonary tuberculosis in Kigali, Rwanda: impact of human immunodeficiency virus infection on clinical and radiographic presentation. Does immune reconstitution syndrome promote active tuberculosis in patients receiving highly active antiretroviral therapy? Variation of chest radiographic patterns in pulmonary tuberculosis by degree of human immunodeficiency virus-related immunosuppression. Immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome: emergence of a unique syndrome during highly active antiretroviral therapy. Tuberculosis immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome in countries with limited resources. New tests for the diagnosis of latent tuberculosis infection: areas of uncertainty and recommendations for research. Sputum processing methods to improve the sensitivity of smear microscopy for tuberculosis: a systematic review.
It has two major surface glycoproteins: (a) one with both hemagglutinin and neuraminidase and (b) the other with cell-fusion protein anxiety symptoms children cheap luvox 100mg visa. The F protein is responsible for fusion of lipid membrane of the virus to the host cell anxiety headache purchase luvox 100 mg on-line. Viral replication Antigenic and genomic properties Viral replication is similar to that of measles virus anxiety symptoms 1 generic luvox 100 mg overnight delivery. A fourfold rise in antibody titer of acute and convalescent sera is diagnostic of acute infection anxiety disorders in children discount 50mg luvox with visa. It has an internal nucleocapsid soluble (S) antigen, which is detected by the complement fixation test. Treatment with formaldehyde, ether, or ultraviolet light also inactivates the virus. These vaccines failed to protect against natural infection by parainfluenza virus. The growth of virus in the cells can be detected by direct immunofluorescence and hemadsorption. Chapter 62 Pathogenesis and Immunity Pathogenesis of mumps Mumps Virus Mumps is an acute infectious disease of children, characterized by acute, nonsuppurative, painful swelling of the salivary glands, caused by mumps virus. Properties of the Virus Morphology Mumps virus shows following features: Infection by mumps virus begins after the entry of the virus into the respiratory tract. Salivary glands, such as parotid glands, show desquamation of necrotic epithelial cells lining the ducts. The virus replicates in these target tissues and then causes a secondary phase of viremia. The virus is spread by viremia throughout the body to kidneys, testes, ovary, pancreas, and other organs. Other rare complications include oophoritis, mastitis, pancreatitis, thyroiditis, arteritis, thrombocytopenia, and pneumonia. Host immunity Humoral immunity is characterized by the appearance of antibody against the soluble S antigen and hemagglutinating antibodies. The antibody against S antigen is the first to appear, within 37 days after the onset of symptoms. The hemagglutinating antibodies directed against hemagglutinin confer lifelong immunity against mumps virus. This also contributes to pathogenesis of the disease and is responsible partially for the symptoms observed during the course of clinical illness. Mumps continues to remain endemic in many countries throughout the world, as the mumps vaccine is used in only 57% of the countries. In the absence of vaccination program, it often occurs as epidemics in children 515 years of age. Epididymo-orchitis is the second most common manifestation in adults, which is usually preceded by parotitis. A patient remains infectious usually from 9 days prior to the onset of parotid swelling as long as 7 days after onset of the swelling. The infection is transmitted by direct person-to-person contact and also by inhalation of respiratory droplets. The unvaccinated people and immunocompromised people are at more risk to infection by mumps virus. The laboratory diagnosis is useful for diagnosis of atypical infection or manifestation of mumps without typical symptoms. Egg inoculation: Egg inoculation is another method, but is a less sensitive method than the cell culture. The virus is identified in amniotic fluid 56 days after inoculation by hemagglutinin inhibition assay for hemagglutinins. Cell culture: Mumps virus can be isolated from clinical specimens by inoculation into monkey kidney cells, human amnion cells, or HeLa cells. The growth of the virus in monkey kidney cells is detected by the presence of multinucleated giant cells. Virus growth in the cells can be detected much earlier by hemadsorption of guinea pig erythrocytes adsorbing the surface of virus-infected cells.
References
- Gabella G: Structure of smooth muscles. In Szekeres L, Gy J, editors: Handbook of experimental pharmacology, vol 111, Berlin Heidelberg, 1994, Springer Verlag, pp 3n34. Gearhart JP, Lee RL, Partin AW, et al: A quantitative histological evaluation of the dilated ureter of childhood. II. Ectopia, posterior urethral valves and prune belly syndrome, J Urol 153:172, 1995.
- Falci DR, da Rosa FB, Pasqualotto AC. Comparison of nephrotoxicity associated to different lipid formulations of amphotericin B: a real-life study. Mycoses. 2015;58(2):104-112.
- Troost, B. (2002). Botulinum toxin-type A (Botox, Allergan, Irvine, CA) therapy for intractable headaches [Abstract]. Presented at the American Headache Society Meeting, Seattle, WA, June 21nJune 23.
- Edwards WD. Classification and terminology of cardiovascular anomalies. In: Moss and Adams' Heart Disease in Infants, Children, and Adolescents: Including the Fetus and Young Adults, 7th edition. Lippincott Williams and Wilkins; 2001, pp. 118-39.
- Messerli FH. Cerebroprotection by hypertension in ischemic stroke: the crumbling of a hypothesis. Circulation. 2007;115(23):2907-2908.
- Abali G, Tokgozoglu L, Ozcebe OI, et al: Which Doppler parameters are load independent? A study in normal volunteers after blood donation, J Am Soc Echocardiogr 18:1260-1265, 2005.
- Amanatkar HR, Chibnall JT, Seo BW, et al: Impact of exogenous testosterone on mood: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized placebocontrolled trials, Ann Clin Psychiatry 26:19n32, 2014.















