Mark K. Wax, MD, FACS, FRCSC
- Professor, Otolaryngology/Head and Neck Surgery
- Professor, Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery
- Program Director
- Director, Microvascular Reconstruction
- Coordinator, Education, AAOHNS(F)
- Department of Otolaryngology/Head and Neck Surgery
- Oregon Health Sciences University
- Portland, Oregon
These requirements are based on the body weight of Mexican children who participated in this study gastritis diet ������ purchase misoprostol 200mcg without a prescription. The average body weight of a 10-year-old child gastritis diet �������� buy misoprostol 200mcg without prescription, as per the Food and Agriculture Organization references gastritis y gases best 200 mcg misoprostol, is 25 kg gastritis and duodenitis cheap 100mcg misoprostol with mastercard. It also provides the iodine intake necessary to maintain the plasma iodide level above the critical limit of 0. Moreover, this level of iodine intake is required to maintain the iodine stores of the thyroid above the critical threshold of 10 mg, below which an insufficient level of iodisation of thyroglobulin leads to disorders in thyroid hormone synthesis (18). Data reflecting either iodine balance or its effect on thyroid physiology can help to define optimal iodine intake. In adults and adolescents in equilibrium with their nutritional environment, most dietary iodine eventually appears in the urine, so the urinary iodine concentration is a useful measure for assessing iodine intake. For this, casual samples are sufficient if enough are collected and if they accurately represent a community (19). Correction of the iodine deficiency will bring all these measures back into the normal range. Recent data from the Thyro-Mobil project in Europe have confirmed these relations by showing that the largest thyroid sizes are associated with the lowest urinary iodine concentrations (20). In practice such maximal efficiency is never obtained and therefore considerably more iodine is necessary. Data from controlled observations associated a low urinary iodine concentration with a high goitre prevalence, high radioiodine uptake, and low thyroidal organic iodine content (23). These requirements have been derived from studies of thyroid function during pregnancy and in the neonate under conditions of moderate iodine deficiency. Thyroid volume progressively increases and is above the upper limit of normal in 10 percent of the women by the end of pregnancy. T4 with iodine was probably administered to the pregnant women to rapidly correct sub-clinical hypothyroidism, which would not have occurred if iodine had been administered alone. Upper limit of iodine intake for different age groups An iodine excess also can be harmful to the thyroid of infants by inhibiting the process of synthesis and release of thyroid hormones (Wolff-Chaikoff effect) (28). The threshold upper limit of iodine intake (the intake beyond which thyroid function is inhibited) is not easy to define because it is affected by the level of iodine intake before exposure to iodine excess. Indeed, long-standing moderate iodine deficiency is accompanied by an accelerated trapping of iodide and by a decrease in the iodine stores within the thyroid (18). In addition, the neonatal thyroid is particularly sensitive to the Wolff-Chaikoff effect because the immature thyroid gland is unable to reduce the uptake of iodine from the plasma to compensate for increased iodine ingestion (29). Iodine intake in areas of moderate iodine deficiency In a study in Belgium, iodine overload of mothers (cutaneous povidone iodine) increased the milk iodine concentration and increased iodine excretion in the term newborns (mean weight about 3 kg). These data indicate that modest iodine overloading of term infants in the neonatal period in an area of relative dietary iodine deficiency (Belgium) also can impair thyroid hormone formation. Iodine intake in areas of iodine sufficiency Similar studies have not been conducted in the United States, where transient hypothyroidism is rarely seen perhaps because iodine intake is much higher.
In between lies a water column that ranges from hundreds to thousands of meters gastritis diet �?��� 200 mcg misoprostol fast delivery, where heterotrophic processes determine the rate of organic matter remineralisation gastritis vs gastroenteritis misoprostol 100 mcg free shipping, and therefore the efficiency of export chronic gastritis medicine cheap misoprostol 100 mcg amex. These long temporal and large spatial scales are enormously challenging for oceanographic research gastritis diet ��� generic 100 mcg misoprostol overnight delivery. Methodological limitations especially apply to experimental approaches in ocean acidification research. Nevertheless, potential sensitivities of organic matter and export production to seawater acidification gather scientific and political attention due to their high potential to affect ecosystem functioning, biogeochemical cycles and global climate. This chapter will provide technical guidelines for the investigation of key processes of the biological carbon pump. Due to the complex nature and the very large variety of potential methods to be applied, only some of the most important aspects can be discussed. Nevertheless, we hope that these will be useful for considering organic and export production in ocean acidification research. As this key process drives important elemental cycles and provides the energy for higher trophic levels, photoautotrophs like phytoplankton and cyanobacteria have been in the centre of ocean acidification research. In order to measure the effect of environmental factors on photosynthesis, including ocean acidification, several different methods have been developed and applied (see also Joint Global Ocean Flux Study reports 27 and 36 at ijgofs. Calibrations are achieved by measuring signals from known concentrations of O2, commonly O2-free and air-saturated (21% O2), and therefore these three approaches yield similar results for photosynthetic O2 evolution (as well as respiration). Since rates are derived from two measurements (before and end of incubation), it is important to choose meaningful time intervals. The latter approach is mostly used in field studies with incubation times in the order of hours to one day. Prior to the measurement of organic carbon, samples are treated with acid to remove all residual inorganic carbon from the filters. This technique can, however, easily be modified to also estimate particulate inorganic carbon production, i. When using the 14C micro diffusion technique (Paasche & Brubak, 1994), estimates for photosynthesis and calcification can be obtained from the same sample (see chapter 12 of this guide). The photosynthetic process can also be examined using variable chlorophyll fluorescence measurements. The techniques used are very sensitive and non-invasive and can hence be used for fieldwork. Thus, they have an important role in marine ecosystems and biogeochemical cycles (Mulholland, 2007). Nitrogen fixation rates can be determined by the acetylene reduction assay (Capone, 1993 and references therein) and the 15N method (Mulholland & Bernhardt, 2005). Acetylene gas is an analog of molecular N2, and the nitrogenase enzyme catalyses reduction of the triple bond in acetylene to double-bonded ethylene. In this assay, a gas chromatograph is used to measure ethylene production after briefly incubating the N2 fixers with added acetylene. The ratio of acetylene reduced to nitrogen fixed is then calculated using a conversion factor (Capone, 1993) and the Bunsen gas solubility coefficient (Breitbarth et al. For the 15N technique, isotopically labelled N2 gas is introduced to an incubation containing diazotrophs, followed by filter harvesting of the labelled biomass. A mass spectrometer is used to determine the 15N values of the samples, which are then used to calculate rates of N2 fixation. While the acetylene method estimates gross nitrogen fixation rate (enzyme potential), the 15N method measures net nitrogen production (nitrogen fixed that stays inside the cells) (Mulholland, 2007). This method only works provided that additional nitrogen sources are known and quantified. However, the general applicability of the Redfield C:N:P ratio to interrelate macro-element fluxes is controversial, and there are numerous examples showing systematic deviation on the organism and species level, with the trophic status of the system, and over time and space. Nevertheless, deviations of the C:N ratio in particulate organic matter generally are within a range of 20 to 30% (Sterner et al. A somewhat larger decoupling of C and N is observed for processes involving inorganic compounds (Banse, 1994). In order to identify potential effects of ocean acidification on element co-cycling affecting export production, researchers might particularly look for (1) systematic changes in element ratios, compared to the Redfield ratio, (2) effects on the availability of limiting nutrients, specifically nitrogen and (3) effects that lead to qualitative changes in organic matter that in turn affect export efficiencies.
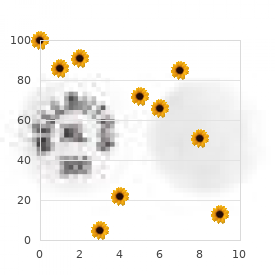
At the time of publication very few ocean acidification studies report using multivariate analyses gastritis diet ����� misoprostol 200 mcg otc. This is surprising because multivariate techniques in general are ideally suited to studies where multiple response variables are measured in the same experimental units gastritis low blood pressure discount 100 mcg misoprostol. Importantly gastritis symptoms empty stomach cheap 200mcg misoprostol visa, these techniques also avoid the inherent problems of increased Type I error rates that arise from multiple testing of separate variables from the same replicate units gastritis symptoms shortness of breath purchase misoprostol 200mcg mastercard. This led to the conclusion that low pH does not only induce a delay in development / reduced growth (see Figure 4. Discriminant Function Analysis of morphometric parameters of larvae of different ages (d since fertilisation) and pH treatments. Grey symbols correspond to the different days (from 1 to 8) in the control (from Dupont et al. We strongly encourage the reader to delve a little deeper into at least one of the excellent texts available on this topic. Experiments in ecology: their logical design and interpretation using analysis of variance. General principles a) Is the design of experiments relevant to the question we intend to answer Experimental design a) Before planning definitive experiments undertake pilot experiments and conduct power analyses to determine the required levels of replication in order to obtain adequate power. Statistical analyses a) Whenever possible, perform power analysis on pilot data to ensure the experimental design has sufficient statistical power, before conducting the main experiment. Near-future levels of ocean acidification do not affect sperm motility and fertilization kinetics in the oyster Crassostrea gigas. Effects of long-term moderate hypercapnia on acidbase balance and growth rate in marine mussels Mytilus galloprovincialis. Impact of supply-side ecology on consumer-mediated coexistence: evidence from a meta-analysis. The case against retrospective power analyses with an introduction to power analysis. From laboratory manipulations to earth system models: scaling calcification impacts of ocean acidification. The main premise for the establishment of these guidelines is that the experiments should represent the conditions of the future ocean as accurately as possible with respect to the carbonate system. Regardless of whether one is working with mixed natural populations of microorganisms, or with monospecific cultures, there are two basic approaches that can be used to carry out manipulations of the carbonate system in small volume experiments: (1) batch and dilute batch cultures in the laboratory, alternatively called grow outs or bioassays in the field and (2) continuous cultures or chemostats and their variations such as turbidostats and cyclostats. A third alternative is to use semi-continuous cultures which are periodically diluted with fresh culture media in order to keep cells in the exponential growth phase. Batch, dilute batch and continuous cultures are best suited to answer different types of questions and have associated advantages and drawbacks that are discussed below. These types of approaches have been used for monospecific cultures in the laboratory and mixed microbial populations in the field (Hutchins et al. The acceptable methods for manipulating the carbonate chemistry have been described elsewhere in this guide to ocean acidification research (chapter 2) and are only briefly summarised here. All of these methods are indistinguishable in terms of their effects on the carbonate chemistry. The method of choice for culture experiments, either an open aerated system or a closed system without headspace (Figure 5. In general, large or fragile phytoplankton, such as for example Trichodesmium erythraeum and dinoflagellate species, might be affected by the turbulence created by aeration. Thus, the effect of aeration and bubble size on growth rate and the general physiology of a phytoplankton species should be assessed in preliminary experiments. The goal of culturing phytoplankton in either batch cultures or chemostats is often to optimise cell yield. This is reflected by the frequent use of nutrient-rich culture media and high cell density at harvest. Ocean acidification research has a different goal; rather to accurately represent the present and future Figure 5.

Next-generation simulation tools will allow reliable predictions of long-term performance of wells and can be used to optimize well completion and monitoring gastritis symptoms vs gallbladder buy misoprostol 200mcg mastercard. Next-generation technologies should result in wells that are safe gastritis acid diet order misoprostol 100mcg line, self-sealing gastritis diet 21 buy misoprostol 100 mcg on-line, and selfdiagnosing over the long term gastritis diet advice nhs generic misoprostol 100 mcg visa. Scientific Challenges Forecasting the containment performance and sealing ability of wells using current approaches involves a high degree of uncertainty, as predictions are based on very simplistic models. To develop new well simulation tools, it is necessary to establish fundamental relationships among parameters affecting well integrity. These tools should be capable of simulating real well conditions, including all the necessary boundary conditions and input parameters- not just simplified models. Laboratory experiments and field investigations of leaking wells can provide characteristic values as input for realistic simulations. Carbon dioxide and formation water are corrosive to common steel pipes and cements used in well completion. In addition, various forces act on the materials, causing stresses that can weaken the interfaces among rock, cement, and steel; these facilitate further corrosion and access of fluids. And it is a scientific challenge to exploit the former for long-term well sealing completions. Current well completion methods do not include or allow provisions for cost-effective, continuous monitoring of well status during well operation and after plugging and abandonment. Research Directions Validating processes and fundamental relationships through field and bench-scale laboratory tests Efforts to improve well integrity are limited by a lack of knowledge of the mechanical and chemical stresses in wells and by the inability to translate existing logging data into accurate images of the annular space, including the distribution of cement and the bonding of cement to interfaces. Current analytical and numerical simulations of well performance emphasize that the results are contingent on assumed stress states in a well. Current logging techniques provide a basis for distinguishing the relative quality of cement but these techniques remain simple qualitative measures of integrity. These must accurately describe the transfer of energy and matter among and within the different domains and take into account the different time and length scales associated with these processes. Some chemical reactions, for example, occur at the time scale at which fluids pass through wells; others that alter the rocks in the well surroundings may need decades or millennia to accumulate geotechnically relevant products and effects. Developing sensor technologies to enable performance monitoring of wells One approach to improved well monitoring is downscaling of logging devices so that they can be used in slim wells or in the annuli between well strings. New sensor applications may emerge from medical applications, marine technologies, soil science, groundwater sampling, and environmental monitoring. Microsensors for measuring physical and chemical properties, measuring leakage, or monitoring corrosion could be built into robust packages required for logging in harsh environments. Data storage, data transmission, and power supply are challenges for long-term in situ monitoring. Other developments for smart monitoring of wells might include micro-reactors for sampling and lab-on-a-chip analyses, or sensors actively exciting surrounding media. Multiple options for determining mechanical and chemical properties are emerging for fiber optics applications and other devices embedded in cement or included in casings. Wireless, autonomous, or remotely controlled mini-loggers would provide options for inspections in currently inaccessible areas. Passive nanosensors could be used as tracers reporting on their passage through the wellbore system. Developing and qualifying smart materials for well integrity the use of smart materials has grown across many industries, creating opportunities for a new generation of well-construction materials with purpose-designed properties for well monitoring and remediation. Self-diagnosis or self-monitoring functions are used in piezoelectric ceramics, shape-memory alloys, and optical fibers. Well monitoring can be enhanced by exploiting self-diagnosing materials with tailor-made properties that allow signal detection through tubing. Technologies such as fiber-reinforced plastics with embedded sensors have been used in structural materials for fracture toughness and detection. Optical fibers wrapped along well casings, pressure-sensitive particles, and microsensors embedded in the well cement could be developed, deployed, and tested at relevant subsurface conditions.
Purchase misoprostol 200mcg with visa. 3DMJ Podcast #72: When the Recovery Diet Ends.
References
- Gundeti MS, Reynolds WS, Duffy PG, et al: Further experience with the vascular hitch (laparoscopic transposition of lower pole crossing vessels): an alternate treatment for pediatric ureterovascular ureteropelvic junction obstruction, J Urol 180:1832, 2008.
- Hill DJ, Feldt RH, Porter C, et al. Protein losing enteropathy after Fontan operation: A preliminary report (Abstract). Circulation. 1989;80:490.
- Choi HJ, Ju W, Myung SK, et al. Diagnostic performance of computer tomography, magnetic resonance imaging, and positron emission tomography or positron emission tomography/computer tomography for detection of metastatic lymph nodes in patients with cervical cancer: meta-analysis. Cancer Sci 2010;101(6):1471-1479.
- Lefebvre G, et al: Primary dysmenorrhea consensus guideline, JOGC 27(12):1117-1146, 2005.
- Scott FB: The artificial urinary sphincter. Experience in adults, Urol Clin North Am 16:105, 1989.















