John D. Bisognano, MD, PhD
- Director of Outpatient Cardiology
- Professor of Medicine
- University of Rochester Medical Center
- Rochester, New York
When test results are inconclusive treatment jerawat di palembang purchase hydrea 500mg with amex, obtain specialist evaluation for precise measurement of peripheral vision treatment under eye bags discount 500 mg hydrea mastercard. Color vision the color vision requirement is met by the ability to recognize and distinguish among red symptoms non hodgkins lymphoma order hydrea 500 mg with visa, amber medicine song 2015 buy hydrea 500mg online, and green, the standard colors of traffic control signals and devices. Additional Evaluation and/or Ancillary Tests Eye trauma and ophthalmic disease can adversely impact visual performance and interfere with safe driving. Some ophthalmic diseases are seen more frequently with increased age or are secondary to other diseases such as diabetes mellitus or atherosclerosis. The clinical setting may not provide the necessary equipment to evaluate ophthalmic diseases adequately. The medical examiner determines if the vision symptoms and signs or underlying disease require evaluation by an ophthalmologist or optometrist. The medical examiner then considers the documented results and the specialist opinion when determining if the vision meets qualification requirements. Certification and Documentation the qualified driver meets all of the following requirements: · Distant acuity of at least 20/40 in each eye, Binocular acuity of at least 20/40, Horizontal field of vision of at least 70° measured in each eye, and the ability to recognize and distinguish among traffic control signals and devices showing standard red, amber, and green colors. The driver who wears corrective lenses to meet the vision qualification requirements must wear corrective lenses while driving. The examiner should advise the Page 56 of 260 driver to carry a spare set of eyeglasses. The driver avoids both stress and delay when lost or damaged eyeglasses or uncomfortable contact lenses can be replaced immediately. Monocular vision Monocular vision occurs when the vision requirements are met in only one eye, with or without the aid of corrective lenses, regardless of cause or degree of vision loss in the other eye. In low illumination or glare, monocular vision causes deficiencies in contrast recognition and depth perception compared to binocular vision. The medical examiner should complete the certification examination of the driver with monocular vision and determine if the driver is otherwise qualified. The driver with monocular vision who is otherwise qualified may want to apply for a Federal vision exemption. Mark the "accompanied by" exemption checkbox and write "vision" to identify the type of Federal exemption. Ophthalmic Preparations Determine if the treatment is having the desired effect of preserving vision that meets qualification requirements without any visual and/or systemic side effects that interfere with safe driving. Categories include: Age-related Macular Degeneration Classifications of agents used to treat age-related macular degeneration include: · Antioxidants and zinc. Anti-allergy (Allergic Conjunctivitis) Classifications of anti-allergy agents used to treat allergic conjunctivitis include: · Oral and topical antihistamines. Antiglaucoma Agents Classifications of agents used to treat glaucoma include: · Prostaglandin analogs. Anti-infective Agents (Bacterial Conjunctivitis) Classifications of anti-infective agents used to treat bacterial conjunctivitis include oral and topical antibiotics. Dry Eyes Classifications of agents used to treat dry eyes include: · Lubricants. Ophthalmic Diseases Cataracts Cataracts are a common cause of visual disturbances in the adult population. The slow, progressive opacification of the crystalline lens of the eye distorts the optical passage of light to the retina resulting in diminished visual acuity. Cataract formation can be accelerated by a number of conditions, including injury, exposure to radiation, gout, certain medications (steroids), and the presence of diabetes mellitus. Glare, particularly during night driving in the face of oncoming headlights, may be an early symptom of cataracts. Glare, diminished overall acuity, contrast, and color resolution are compounded by the lightscattering effect of the cataracts. The abnormal regulation of intraocular pressure can result in gradual progressive atrophy of optic nerve cells. The development of chronic elevated intraocular pressure is generally painless, and the gradual loss of peripheral visual field can progress significantly before symptoms are noticed. Glaucoma may also affect a number of subtler visual functions, such as redirection of visual attention, night vision, and color vision. With glaucomatous damage, Snellen acuity test results may not be affected, but peripheral field test results may show deficits.
Oropharyngeal anthrax: · Infection is characterized by painful neck swelling and fever treatment pneumonia buy hydrea 500 mg overnight delivery. Meningeal anthrax: 17 · Infection is characterized by fever medications used to treat fibromyalgia purchase hydrea 500mg with amex, malaise symptoms 3 days before period purchase hydrea 500 mg mastercard, meningeal signs medicine 4h2 pill buy 500 mg hydrea with mastercard, hyperreflexia, and delirium, stupor, or coma. Published case-fatality rates are as follows: cutaneous <1%, gastrointestinal 25% to 60%, inhalational 46% and injectional 21 33%. Although Anthrax is not endemic to Panama, imported, expatriate or other presentations of the disease have been associated with this country. An acute illness characterized by cough, wheezing and eosinophilia; adult worms are associated with abdominal pain (occasionally obstruction), pancreatic or biliary disease; highest rates among children and in areas of crowding and poor sanitation. Worms may also invade and obstruct the biliary duct (pancreatic-biliary ascariasis), producing abdominal pain, which 20 21 22 may be associated with ascending cholangitis, acute or recurrent pancreatitis, pancreatic pseudotumor or 23-26 obstructive jaundice. Page 29 of 388 Ascariasis Infectious Diseases of Panama - 2013 edition References 1. Cutaneous lesions often arise in crops and resemble the lesions of verruga peruana. An aerobic gram-positive bacillus Soil Processed & dried foods None Food 2h - 9h (range 1h - 24h) No practical test available. Supportive As for adult Usually follows ingestion of rice or other vegetables; vomiting within 1 to 6 hours and/or diarrhea within 6 to 24 hours; no fecal leucocytes. Diarrheal form: the onset of watery diarrhea, abdominal cramps, and pain occurs 6 to 15 hours after consumption of contaminated food. Emetic form: the emetic type of food poisoning is characterized by nausea and vomiting within 0. Associated conditions: 5-7 8 9 Sequelae of bacterial vaginosis include preterm birth and neonatal distress, low birth weight, chorioamnionitis, 10 11 12 cervicitis, scalp abscess of the newborn, an increased risk of late miscarriage and maternal infection. Gardnerella vaginalis has rarely been associated with balanitis, urethritis, urinary tract infections, asymptomatic bacteremia 22 and infectious endocarditis in adult males. Cases of osteomyelitis, discitis and septic arthritis due to Gardnerella vaginalis have been reported. Ciliate (Ciliophora), Litostomatea: Balantidium coli Pig Non-human primate Rodent None Water Food 1d - 7d (range 1d - 60d) Microscopy of stool or colonic aspirates. Balantidiose, Balantidiosis, Balantidium coli, Balantidosis, Balindosis, Ciliary dysentery. Thus stool specimens should be collected repeatedly, and immediately examined or preserved. A facultative gramnegative coccobacillus Cat Possibly tick Flea (cat flea = Ctenocephalides) Cat scratch Plant matter (thorn, etc) 3d - 14d Visualization of organisms on Warthin Starry stain. Azithromycin 500 mg day 1, then 250 daily X 4 days Alternatives: Clarithromycin, Ciprofloxacin, Sulfamethoxazole/trimethoprim Aspiration of nodes as necessary. Azithromycin 10 mg/kg day 1, then 5 mg/kg daily X 4 days Tender suppurative regional adenopathy following cat scratch (usually kitten); fever present in 25%. Symptoms: Following an incubation period of 3 to 10 days, a small skin lesion appears consisting of a macule, papule, pustule or vesicle. Page 36 of 388 Bartonellosis - cat borne Infectious Diseases of Panama - 2013 edition · B. In one case, Bartonella koehlerae infection was associated with depression, anxiety, mood swings, severe headaches, muscle 48 spasms, interphalangeal joint stiffness, decreased peripheral vision, diminished tactile sensation and hallucinations. Alternatives: Clarithromycin, Azithromycin Headache, myalgias, shin pain, macular rash, splenomegaly; endocarditis & bacteremia seen; relapse common; often associated with poor hygiene & crowding. Bartonella alsatica, Bartonella bovis, Bartonella capreoli, Bartonella doshiae, Bartonella elizabethae, Bartonella grahamii, Bartonella quintana, Bartonella rochalimae, Bartonella schoenbuchensis, Bartonella tamiae, Bartonella vinsonii, Bartonella vinsonii berkhoffii, Bartonella volans, Bartonella washoensis, Candidatus Bartonella mayotimonensis, Candidatus Bartonella melophagi, Candidatus Bartonella merieuxii, Candidatus Bartonella rochalimae, Five day fever, His-Werner disease, Meuse fever, Quintan fever, Quintana fever, Shank fever, Shin fever, Shinbone fever, Trench fever, Volhynian fever. Subclinical bacteremia is common among immuno-competent persons with animal and arthropod contact. Bartonella quintana (formerly Rochalimaea quintana) and related bacteria may also produce bacillary angiomatosis 2-5 6 7 8 9 (discussed separately in this module), bacteremia, endocarditis, myocarditis, uveitis, neuroretinitis or chronic lymphadenopathy.
Levels in alveolar macrophages (median concentration 81 mg/L) significantly exceeded plasma levels 8 hours after dosing and maintained elevated levels 24 and 48 hours after dosing (23 mg/L and 2 symptoms 2015 flu cheap 500 mg hydrea. Tigecycline is also distributed widely in tissues medications 2355 buy hydrea 500 mg overnight delivery, with a steady-state volume of distribution of 7 to 10 L/kg symptoms vitamin b12 deficiency buy 500 mg hydrea amex. Thirty percent to 40% of an oral dose of clarithromycin is excreted in the urine either unchanged or as the active 14-hydroxy metabolite medicine recall cheap hydrea 500 mg on-line. In patients with moderate to severe renal impairment (ie, creatinine clearance <30 mL/min), the dose should be reduced. In patients with mild to moderate renal impairment, there was no significant change in the pharmacokinetics of telithromycin. In healthy male volunteers who received 14C-tigecycline, 59% of the radioactive dose was recovered in the feces and 33% recovered in the urine. Dose adjustment is not necessary based on age, sex, renal impairment, or mild to moderate hepatic impairment (Child Pugh class A-B). In vitro susceptibility testing does not account for the antimicrobial activity of the active 14-hydroxy metabolite and may underestimate the activity of clarithromycin. Comparative in vitro susceptibility data for erythromycin, clarithromycin, azithromycin, and telithromycin are shown in Table 3. Compared with erythromycin, clarithromycin demonstrates equal or better in vitro activity against gram-positive organisms, whereas azithromycin is two- to fourfold less active. Table 2 Susceptibility test result interpretative criteria Clarithromycin S S aureus Streptococcus spp, including pneumoniae Enterococcus faecalis Haemophilus spp Enterobacteriaceae Anaerobes 2 0. Performance standards for antimicrobial susceptibility Testing; TwentyFirst Informational Supplement; 2011. Macrolides, Ketolides, and Glycylcyclines 767 Table 3 Comparative in vitro activities of macrolide/ketolide antibiotics* Organism Gram-positive aerobes Streptococcus pyogenes erythromycin susceptible ermA resistance ermB resistance mefA resistance Streptococcus pneumoniae erythromycin sensitive erythromycin resistant ermB erythromycin resistant mefA Gram-negative aerobes Haemophilus influenzae Moraxella catarrhalis Legionella pneumophila Neisseria gonorrhoeae Other pathogens Chlamydophila pneumoniae Mycoplasma pneumoniae 0. Azithromycin is more active against Campylobacter jejuni than erythromycin or clarithromycin, whereas clarithromycin has greater activity against H pylori. A 5day course of the extended-release formulation of clarithromycin, azithromycin, or telithromycin is equally as effective as a 10-day course of penicillin for the treatment of streptococcal pharyngitis. Dosage for treatment of acute maxillary sinusitis is either 500 mg every 12 hours with the immediate-release tablets for 14 days or 2 В 500 mg every 24 hours with the extended-release tablets for 7 days. The recommended adult dose is 500 mg on the first day followed by 250 mg once daily on days 2 through 5. For children, the following azithromycin dosing regimens can be used for the treatment of otitis media: 30 mg/kg as a single dose, 10 mg/kg once daily for 3 days, or 10 mg/kg on the first day followed by 5 mg/kg on days 2 through 5. Azithromycin is also approved for the treatment of acute bacterial sinusitis; the adult dose is either 500 mg daily for 3 days or a single 2-g dose of the extendedrelease formulation and for children it is 10 mg/kg once daily for 3 days. Studies have shown equal efficacy of clarithromycin compared with ceftibuten, cefaclor, cefuroxime axetil, and cefixime for the treatment of lower respiratory tract infections. Telithromycin was equally effective when compared with a 10-day course of high-dose amoxicillin, twice-daily clarithromycin, or a 7- to 10-day course of trovafloxacin. Monotherapy with intravenous azithromycin was equally effective as a respiratory fluoroquinolone or a b-lactam plus macrolide regimen for patients hospitalized with community-acquired pneumonia. Surveillance studies in the United States revealed that 28% to 35% of S pneumoniae isolates are macrolide resistant. In the United States, 50-60% of the macrolide-resistant isolates exhibited low-level erythromycin resistance (16 mg/L) via expression of the mef(A) gene, and nearly 2025% expressed the mef(A) gene and the erm(B) gene, resulting in high-level resistance. One surveillance study of S pneumoniae isolates from Taiwan revealed that 2% were resistant to telithromycin and 96% were macrolide resistant. In a prospective cohort study of patients who were discharged from emergency departments and prescribed clarithromycin for the treatment of community-acquired pneumonia, macrolide resistance among S pneumoniae isolates did not affect outcomes. Given the possibility of treatment failure, most guidelines recommend combining a macrolide with a b-lactam if risk factors are present for drug-resistant S pneumoniae. Whether this translates into a therapeutic advantage in the empiric treatment of respiratory tract infections, especially when drug-resistant S pneumoniae is of concern, needs to be determined. In the outpatient setting, recommended antimicrobial therapy for patients who were previously healthy and have no risk factors for drugresistant S pneumoniae includes any macrolide (erythromycin, azithromycin, clarithromycin). Recommended outpatient therapy for individuals who have comorbid conditions, have received antibiotics within the previous 3 months, or have other risk factors for drug-resistant S pneumoniae includes a macrolide in combination with a b-lactam. For patients who require hospitalization, a macrolide combined with a b-lactam is one of the preferred regimens recommended. The approved dose of azithromycin for treatment of lower respiratory tract infections is 500 mg the first day followed by 250 mg for days 2 through 5.
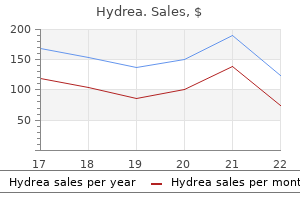
Order 500 mg hydrea. Moments when SHINee's vocals saved me.
References
- Marsh JN, Senpan A, Hu G, et al. Fibrin-targeted perfluorocarbon nanoparticles for targeted thrombolysis. Nanomedicine (Lond) 2007;2:533-43.
- Speight P, Barrett AW. Prognostic factors in malignant tumors of the salivary glands. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg 2009;47: 587-593.
- Melacini P, Maron BJ, Bobbo F, et al: Evidence that pharmacological strategies lack efficacy for the prevention of sudden death in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, Heart 93:708, 2007.
- Meier-Ewert HK, Gray ME, John RM. Endocardial pacemaker or defibrillator leads with infected vegetations: a single-center experience and consequences of transvenous extraction. Am Heart J 2003;146:339-344.
- Krieger NR, Shochat SJ, McGowan V, et al: Early hernia repair in the premature infant: long-term follow-up, J Pediatr Surg 29:978, 1994.
- Ganz R, Klaue K, Vinh TS, Mast JW. A new periacetabular osteotomy for the treatment of hip dysplasias. Technique and preliminary results. Clin Orthop Relat Res 1988(232):26-36.
- Coman D, McGill J, MacDonald R, et al. Congenital disorder of glycosylation type 1a: Three siblings with a mild neurological phenotype. J Clin Neurosci 2007;14:668.