David J Alexander MBBs FRCS MS
- Consultant colorectal surgeon and Clinical
- director of cancer service
- York Hospital NHS Trust, York, UK
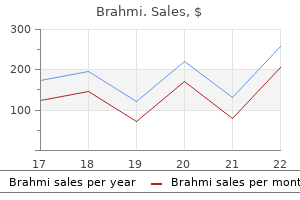
Once the provider has successfully completed the class symptoms 2 weeks after conception cheap 60caps brahmi mastercard, the provider will be sent written notification with instructions for requesting the announced initial licensing survey symptoms 6 months pregnant buy discount brahmi 60caps line. The license is valid until the expiration date shown on the license medicine 93 7338 discount brahmi 60 caps with amex, unless the license is modified medications safe during pregnancy cheap 60 caps brahmi, revoked, suspended, or terminated. The Department also may perform an on-site survey and inspection upon annual renewal of a license. Appropriateness of services provided including content, intensity, frequency, and recipient input and satisfaction. The presence of the personal outcomes as defined and prioritized by the recipient/guardian. Centers are expected to provide transportation to any client within their licensed region, but no participant, regardless of their region of origin, may be in transport for more than 1 hour on any single trip. A full-time director is required to manage the center and ensure that all services provided are consistent with accepted standards of practice and that center policies are executed. The director must be accessible to center staff or to any representative of the Department of Health and Hospitals conducting an audit, survey, monitoring activity, or research and quality assurance. The social service designee/social worker and the program manager must be employed at least 10 hours a week in their respective capacities. The latter three positions are considered to be "key staff," any one of whom may also serve as the director. Centers with a licensed capacity of 15 or fewer participants may designate one full-time staff person or full-time equivalent person to fill up to three "key staff" positions, and must employ at least one full-time person or full-time equivalent to fulfill key staff requirements. Centers with a licensed capacity to serve 16-30 participants must employ at least two full-time persons or full-time equivalents to fulfill key staff requirements, and may designate one full-time staff person or full-time equivalent person to fill up to , but no more than, two "key staff" positions. Each key staff position must be filled with a full-time person or full-time equivalent. The center must also designate one staff member who is employed at least 10 hours per week as a food service supervisor who is responsible for meal preparation and/or serving. A direct service worker is an unlicensed staff person who has face-toface direct contact with participants and provides personal care or other services and support to them to enhance their well-being. Volunteers and student interns are considered a supplement to the required staffing component and must be directly supervised by a paid staff member. They must also receive orientation and ongoing in-service training at least quarterly. The direct service worker-to-participant ratio is a minimum of one full-time direct service worker to every nine participants. A staff member certified in cardiovascular pulmonary resuscitation must be on the premises at all times while participants are present. A center must ensure that each direct care staff person completes no less than 20 hours of face-to-face training per year. Orientation and normal supervision will not be considered to meet this requirement. Location of Licensing, Certification, or Other Requirements Department of Health and Hospitals website: Licensing, Regulations, Policies, and Procedures for Adult Day Health Care Centers /new. Providers may be licensed to offer more than one program, as long as record-keeping is distinct. The program is maintained or carried out on a regular basis by a person or persons in a private dwelling or other facility, for any part of a day, for at least 2 hours a day, for more than two adults 19 years of age or older who are not blood relatives and are coming to the facility for up to 7 days a week for the express purpose of participating in the program. Therapeutic activities means restorative activities designed to maintain or improve the quality of life or delay skill deterioration. Participants in both a daytime program and a night program are limited to seven dates of participation in a 7-day period. Providers may discharge participants if they endanger the safety and/or health of other program participants. In addition, to be eligible for the three non-Medicaid programs and for MaineCare, individuals must have a recognized or diagnosed need verified through a standard functional assessment (Medical Eligibility Determination Form). The Department may make unannounced visits to evaluate compliance with regulations and to talk privately with participants. For example, for participants dually-eligible for Medicare and Medicaid, Medicare-as first payer-could pay for the various therapies, counseling, and social services. Otherwise, under the Medicaid waiver program, participants can choose from a menu of services up to the amount of their waiver cost cap.
More specifically symptoms heart attack women buy brahmi 60 caps, this intervention galvanizes communities and educates parents about positive and effective parenting practices to improve their parenting skills to prevent child maltreatment and protect children from the traumatic effects of violence symptoms of appendicitis order 60caps brahmi. In a randomized evaluation study of the program 5 medications post mi brahmi 60 caps without a prescription, Portwood and colleagues (Portwood et al treatment 12mm kidney stone discount brahmi 60caps with mastercard. The Triple P program is a multi-level intervention, in which parents with children ages 0-12 learn positive and supportive parenting practices while normalizing parents who need to develop their parenting skills and providing appropriate tools and knowledge to raise healthy children. The first level of Triple P uses media campaigns targeting parents seeking parenting help, which normalizes seeking parenting help and markets the other levels of the program. The subsequent levels of this program will be described below as they fall within the selective and indicated interventions discussed below. Triple P has been evaluated before, but the evaluations will be discussed below as those findings are not exclusive to this first level of the program; they evaluate the whole program. Mothers who received nurse home visits also reported fewer subsequent pregnancies and a longer time between pregnancies. Participants with fewer economic, social and emotional resources have shown more positive impacts than those with more resources. In addition, subgroup positive impacts have been found for birth weight and preterm birth for mothers under 17 and those who reported smoking five or more cigarettes a day during pregnancy. Children who were 48 born to mothers with low psychological resources in the nurse-visited group had higher levels of language development and higher mental development. Selective preventive interventions the second level includes selective preventive interventions targeted to parents at risk for developing negative parent-child relationships, ineffective parenting strategies, and maltreating their offspring. Because research finds that children from homes experiencing family violence are likely to display externalizing behaviors, conduct and oppositional defiant disorder, and aggressive interactions with peers and that parenting practices can either buffer the effects of family violence, the non-abusive parent can benefit from selective preventive parenting interventions. Thus, a selective preventive intervention could target parents from families affected by domestic violence to gain effective parenting skills to buffer the negative effects of this kind of violence on children. Additionally, this intervention could educate non-abusive parents about the sequel and effects of family violence and provide resources and support for parents parenting a child who has history witnessing family violence. The objective of this program is to help parents and children improve their relationship, which may have been affected by family violence, and address the traumatic experience of domestic violence. Another example of a program targeting children and parents affected by domestic violence is the Kids Club & Moms Empowerment program, which serves 6-12 year old children and their mothers. The Kids Club helps children affected by family violence to learn to cope with this situation so that they do not internalize or externalize their experience and develop accepting attitudes about violence. The Moms Empowerment component helps mothers be effective parents even under this stressful situation, learn ways to reduce the stress that these family situations brings to them while getting support and resources. Indicated Preventive Interventions the third level of the violence preventive intervention would include preventive interventions targeted to high-risk parents who have a history of ineffective parenting and child maltreatment, and/or who have children who have problems with aggression, conduct disorder, or are violent. This program was recently adapted to target families with a history of physical 49 abuse for parents to learn effective and appropriate parenting practices, and improve parent-child interactions and relationships. A child who has experienced traumatic stress is often less able or unable to selfregulate, and may experience feelings of traumatic stress at times when the child is not actually threatened, for example, at school or in a safe residential placement. Bullying is both a form of violence in and of itself, as well as a risk factor for other more-serious forms of violence (Nansel et al. In addition, any bullying involvement, including as the target, aggressor, or witness, has been linked to significant negative academic, social, psychological, and behavioral outcomes that may persist from childhood into adulthood (Bogart et al. Bullying can also occur in a variety of contexts, including through electronic technology. Emerging research also suggests a high level of overlap between contexts, with 84 percent of those who reported being cyberbullied in 2009 also reporting being bullied through more traditional means (Robers et al. Generally, nationally representative statistics indicate that between 20 and 30 percent of students report being bullied (Kann et al. Bullying involvement appears to peak in early adolescence, and a national study of middle and high school students suggested that the highest rate of bullying occurred in 6th grade (Neiman, 2011; Stuart-Cassel, Terzian, & Bradshaw, 2013). Although rates of bullying victimization have been relatively stable from 2005 through 2011, differences emerge in different forms of bullying. Rates of physical bullying victimization among children ages 12-18 have decreased from 9 percent in 2005 to 8 percent in 2011, while rates of social bullying victimization (being the subject of rumors and excluded from activities on purpose) have increased from 15 percent to 18 percent and from five percent to six percent, respectively (Robers et al. Namely, teachers are both unlikely to identify relationally aggressive behaviors as bullying and unlikely to be aware of the behavior should it occur (Catherine P. Children may also be more hesitant to report social bullying or may be more likely to think they should deal with the bullying without assistance from adults (Catherine P.
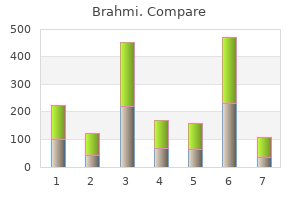
Washer-decontaminators/disinfectors act like a dishwasher that uses a combination of water circulation and detergents to remove soil medications diabetic neuropathy buy brahmi 60caps low price. These units sometimes have a cycle that subjects the instruments to a heat process symptoms ketosis discount brahmi 60 caps amex. Washer-disinfectors are generally computer-controlled units for cleaning symptoms 5 days before your missed period brahmi 60 caps otc, disinfecting medicine you can overdose on buy brahmi 60caps lowest price, and drying solid and hollow surgical and medical equipment. Detailed information about cleaning and preparing supplies for terminal sterilization is provided by professional organizations 453, 454 and books 455. Studies have shown that manual and mechanical cleaning of endoscopes achieves approximately a 4log10 reduction of contaminating organisms 83, 104, 456, 457. Thus, cleaning alone effectively reduces the number of microorganisms on contaminated equipment. When manual methods were compared with automated methods for cleaning reusable accessory devices used for minimally invasive surgical procedures, the automated method was more efficient for cleaning biopsy forceps and ported and nonported laparoscopic devices and achieved a >99% reduction in soil parameters. Enzymes, Last update: May 2019 37 of 163 Guideline for Disinfection and Sterilization in Healthcare Facilities (2008) usually proteases, sometimes are added to neutral pH solutions to assist in removing organic material. Enzymes in these formulations attack proteins that make up a large portion of common soil. Cleaning solutions also can contain lipases (enzymes active on fats) and amylases (enzymes active on starches). Enzymatic cleaners are not disinfectants, and proteinaceous enzymes can be inactivated by germicides. As with all chemicals, enzymes must be rinsed from the equipment or adverse reactions. Neutral pH detergent solutions that contain enzymes are compatible with metals and other materials used in medical instruments and are the best choice for cleaning delicate medical instruments, especially flexible endoscopes 457. Alkalinebased cleaning agents are used for processing medical devices because they efficiently dissolve protein and fat residues 464; however, they can be corrosive 457. Some data demonstrate that enzymatic cleaners are more effective than neutral detergents 465, 466 in removing microorganisms from surfaces but two more recent studies found no difference in cleaning efficiency between enzymatic and alkaline-based cleaners 443, 464. Another study found no significant difference between enzymatic and non-enzymatic cleaners in terms of microbial cleaning efficacy 467. Although the effectiveness of high-level disinfection and sterilization mandates effective cleaning, no "real-time" tests exist that can be employed in a clinical setting to verify cleaning. If such tests were commercially available they could be used to ensure an adequate level of cleaning. Validation of the cleaning processes in a laboratory-testing program is possible by microorganism detection, chemical detection for organic contaminants, radionuclide tagging, and chemical detection for specific ions 426, 471. During the past few years, data have been published describing use of an artificial soil, protein, endotoxin, X-ray contrast medium, or blood to verify the manual or automated cleaning process 169, 452, 474-478 and adenosine triphosphate bioluminescence and microbiologic sampling to evaluate the effectiveness of environmental surface cleaning170, 479. At a minimum, all instruments should be individually inspected and be visibly clean. Last update: May 2019 38 of 163 Guideline for Disinfection and Sterilization in Healthcare Facilities (2008) Disinfection Many disinfectants are used alone or in combinations. These include alcohols, chlorine and chlorine compounds, formaldehyde, glutaraldehyde, ortho-phthalaldehyde, hydrogen peroxide, iodophors, peracetic acid, phenolics, and quaternary ammonium compounds. In most instances, a given product is designed for a specific purpose and is to be used in a certain manner.
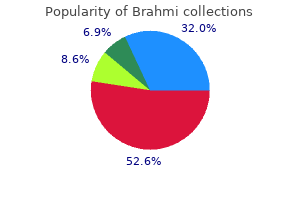
The paradox of social organization: networks medications causing thrombocytopenia cheap 60caps brahmi mastercard, collective efficacy treatment medical abbreviation effective 60 caps brahmi, and violent crime in urban neighborhoods medicine used to treat bv generic 60 caps brahmi with amex. Collective Efficacy and Crime in Los Angeles Neighborhoods: Implications for the Latino Paradox medicine vs medication purchase brahmi 60caps line. The effects of adolescent health-related behavior on academic performance: A systematic review of the longitudinal evidence. Short-term and long-term effects of violent media on aggression in children and adults. Social information processing as a mediator between cognitive schemas and aggressive behavior in adolescents. Risk factors for femicide in abusive relationships: Results from a multiste case control study. Multiple contextual levels of risk for peer victimization: Implications for prevention and intervention efforts. Randomized Trial of a Cellular Phone-Enhanced Home Visitation Parenting Intervention. Intimate partnet violence during pregnancy and 1-year postpartum Journal of Family Violence, 22(7), 609-619. Separate and cumulative effects of adverse childhood experiences in predicting adult health and health care utilization. Predictors of bullying and victimization in childhood and adolescence: A meta-analytic investigation. Impact of a universal school-based violence prevention program on violent delinquency: Distinctive benefits for youth with maltreatment histories. Development, evaluation and national implementation of a school-based program to reduce violence and related risk behaviours: Lessons from the Fourth R. Three-month Follow-up of Brief Computerized and Therapist Interventions for Alcohol and Violence Among Teens. Electronic dating aggression among middle school students: demographic correlates and associations with other types of violence. Understanding teen dating violence: practical screening and intervention strategies for pediatric and adolescent healthcare providers. An Examination of the Factors Related to Dating Violence Perpetration Among Young Men and Women and Associated Theoretical Explanations: A Review of the Literature. Aggressive, rejected, and delinquent children and adolescents: a comparison of their friendships Aggression and Violent Behavior, 9, 75-104. A new protocol for screening adults presenting with their own medical problems at the Emergency Department to identify children at high risk for maltreatment. Family school and behavioral antecedents to early adolescent involvement with antisocial peers. From antisocial behavior to violence: a model for the amplifying role of coercive joining in adolescent friendships. Peer rejection and social information-processing factors in the development of aggressive behavior problems in children. Data Resource Center for Child and Adolescent Health Retrieved 8/22/2014, from Incorporating recognition and management of perinatal and postpartum depression into pediatric practice. Prevalence of Insufficient, Borderline, and Optimal Hours of Sleep Among High School Students -United States, 2007. Effectiveness of mass media campaigns for reducing drinking and driving and alcoholinvolved crashes: a systematic review. The Good Behavior Game: A Best Practice Candidate as a Universal Behavioral Vaccine. Suicidal Ideation and School Bullying Experiences After Controlling for Depression and Delinquency Journal of Adolescent Health, 53(1), S27-S31. Examination of peer-group contextual effects on aggression during early adolescence. Bullying, Sexual, and Dating Violence Trajectories From Early to Late Adolescence: U. Adolescent Substance Use and Suicidal Behavior: A Review With Implications for Treatment Research.
60caps brahmi with mastercard. Little girl's stomach flu symptoms actually early signs of brain tumor.
References
- Mammen AL, Amato AA. Statin myopathy: a review of recent progress. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2010;22:644-650.
- Kinoshita H, Iranami H, Fujii K, et al: The use of bone cement induces an increase in serum astroglial S-100B protein in patients undergoing total knee arthroplasty, Anesth Analg 97:1657, 2003.
- Casuscelli J, Schmidt S, DeGray B, et al: Analysis of the cytoplasmic interaction between polycystin-1 and polycystin-2, Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 297(5):F1310nF1315, 2009.
- Ball NJ, Urbanski SJ, Green FH, Kieser T. Pleural multicystic mesothelial proliferation. The so-called multicystic mesothelioma. Am J Surg Pathol 1990;14(4):375-8.
- Williams DR, Reardon K, Roberts L, et al. A new dominant distal myopathy affecting posterior leg and anterior upper limb muscles. Neurology. 2005;64:1245-1254.
- Miller WL: Fetal endocrine therapy for congenital adrenal hyperplasia should not be done, Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab 29(3):469n483, 2015.
- Schlossberg SM, Vaughan ED: The mechanism of unilateral post-obstructive diuresis, J Urol 131(3):534n536, 1984.